What impact does flexible PCB have on our life?
08 September 2023
Views: 540
With the continuous development of technology, electronic devices have become smaller and more portable. Traditional rigid PCB are no longer able to meet all performance requirements. In this context, flexible PCB have emerged as a new trend in electronic devices.
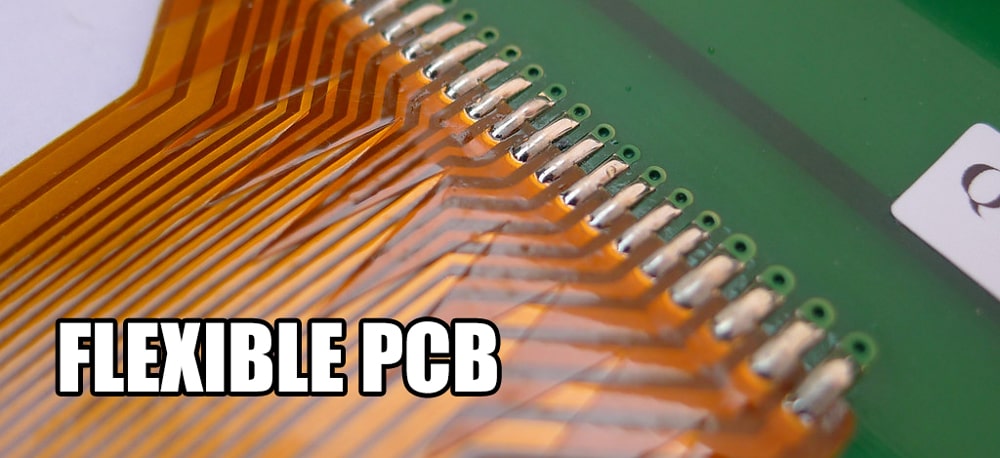
What is a flexible PCB?
The origin of flexible PCBs can be traced back to the 1970s when the first flexible circuit board was developed as a substitute for wire harnesses in automotive applications. Over the years, flexible PCBs have made significant advancements, greatly improving in terms of performance, reliability, and manufacturability. They have now become an integral part of various consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive components, and aerospace systems.
A flexible PCB (FPCB), also known as a Flexible Printed Circuit Board, is a type of flexible and thin flat circuit board. Compared to traditional rigid PCBs, FPCBs allow for bending or deformation during use while maintaining their shape and functionality.
The structure of a flexible printed circuit board typically consists of three key components: a flexible polymer film, conductive circuit traces, and an adhesive. The flexible film is usually made of polyimide and serves as the foundation for the PCB. Then, conductive circuit traces, typically made of copper, are added using chemical etching or laser ablation techniques. Finally, these two layers are bonded together using an adhesive. The result is a PCB that can be bent, twisted, and flexed in ways that traditional rigid PCBs cannot achieve. This flexibility opens up a whole new world of possibilities for electronic design, making devices smaller, lighter, and more compact.
Key technical parameters of FPCBs include:
Substrate Material: FPCBs primarily use materials such as polyester film and polyurethane film as substrates, offering higher flexibility.
Trace Width: The minimum trace width of FPCBs can be as small as below 50μm.
Bending Radius: FPCBs can maintain continuous bending, typically with a bending radius as small as 2mm.
Number of Layers: Commonly, FPCBs have one or two layers of traces, but to achieve higher density, multilayer stacking technology can be employed, with up to 25 layers of traces.
Conductive Material: FPCB traces mainly use copper or gold-plated copper as the conductor material.
Thickness: FPCBs generally have a thickness of 0.1mm or less, with the thinnest reaching 0.02mm.
The main advantages of flexible PCBs include:
Smaller size: Flexible PCBs allow for free bending, enabling electronic devices to be designed in smaller form factors.
Lighter weight: By using lighter materials, the weight of electronic devices can be reduced, making them ideal for portable and mobile applications.
Safety: Flexible PCBs can absorb impacts through bending when subjected to external forces, enhancing device safety.
Applications of flexible PCBs include:
Wearables: Flexible PCBs provide an ideal solution for components in wearable devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and healthcare monitors that need to conform to the human body contours, offering the necessary flexibility and durability.
Consumer Electronics: From display panels and smartphones to laptops, flexible PCBs are increasingly used in consumer electronic products. The trend towards more compact and thinner designs is driving the adoption of flexible PCBs.
Automotive: Flexible printed circuit boards have also found their place in the automotive industry, used in applications such as control systems, entertainment systems, and safety features. They are highly valued for their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, vibrations, and high temperatures.
Medical: Flexible PCBs play a crucial role in medical devices, including implantable medical devices, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.
Aerospace and Defense: The aerospace and defense industries value flexible PCBs for their lightweight and space-saving characteristics. They are used in a wide range of applications, from satellites and spacecraft to military equipment and systems.
In conclusion, flexible PCBs represent a significant advancement in modern electronic devices, meeting the increasing demand for smaller, more portable, and high-performance electronic products. Flexible PCBs will continue to play an increasingly important role in the electronics industry. Whether it's wearable technology, consumer electronics, or automotive applications, if you have any projects requiring the manufacture of flexible PCBs, please feel free to contact us!


